▪ Ethylene ▪ Strigolactone ▪ Gibberellin ▪ Brassinosteroid ▪ Abscisic Acid ▪
Hormone
Cytokinin (CK)
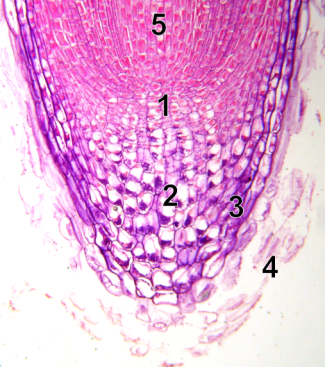
cytokinin is synthesized in the greatest amounts in root tips - A Wikimedia Commons Image
Chemical Structure
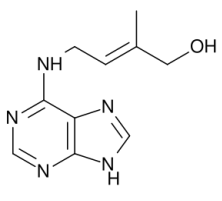
Zeatin
- a wikimedia commons image
Speculative Overall Role
Root nutrition other than water abundance signal
What is cytokinin's speculative
complementary deficiency signal?
Strigolactone
If overall speculative role is
true, where, when and which
cells should synthesize
cytokinin?
Well fertilized plants should have high CK levels, plants living in poor soils should have low levels. CK should be mostly made in meristematic cells and much less so as cells mature. CK should be made when a cell has more than enough essential minerals to support both it any cell dependent on it for mineral acquisition. Thus CK is always an indication that growth amounts of minerals are being procured by the plant and if conditions warrant, that the plant has enough minerals to grow at least in the specific cell where the CK is. (Root cells are responsible for acquiring minerals for both it and similar size cells in the root. Conversely a shoot cell is only responsible to itself for it own mineral nutrition levels).
If overall speculative role is true, what
should exogenous cytokinin treatment produce?
Should induce strigolactones, because CK up regulates various processes limited by minerals. Exogenously applying CK leads the plant to falsely believe that it has high levels of minerals, thus engaging all sorts of reactions that use or are normally limited by mineral levels, thus further depleting what may simply be a homeostatic level of the existing fertilizers and moving this level into the deficiency range.
If overall speculative role is true, what
should cytokinin inhibit and stimulate?
Should induces new shoot growth, just like SA. Especially if SA is also present, CK should inhibit root growth because high SA and CK levels are an indication of at least a short term lack of need to expand the roots.
If overall speculative role is true,
how should
cytokinin affect storage?
CK should cause excess minerals to be stored in vacuoles, storage proteins and tubers for less propitious times.
If overall speculative role is true,
how should cytokinin be transported?
CK may be expected to travel in the direction of the shoots, away from the roots and particularly away from root meristems. Regions of a cell or tissue or plant part that contains high CK, may particularly attract fertilizer type minerals and transport of important minerals may follow active or passive CK transport up a plant in the xylem or other tissue.
If overall speculative role is true, how should
cytokinin affect attraction and repulsion?
Should attract all nutrients and abundance hormones/signals to a cell and repel deficiency hormones/signals.
If overall speculative role is true, how
should
cytokinin affect apical dominance?
Should induce root apical dominance along with SA, however the possibility exists for two dominant apices if one is particularly good at fertilizer absorption (in good soil) and one good at water harvesting (in the moist part of the soil). CK may break shoot apical dominances under conditions of low JA and IAA.
If overall speculative role is true, how
should
cytokinin affect Cell Division?
Along with IAA and JA and Salicylic acid, CK should be necessary for cell division. If there are some plant callus lines that will divide with only auxin and cytokinin present, it is because these cell lines are mutants that produce SA and JA natively. Alternatively these latter two hormones are unknowingly being included with other nutrients/vitamins that are also added to calluses to get them to divide.
If overall speculative role is true, how
should
cytokinin affect senescence?
Should protect plant tissue from senescence, particularly shoot tissue.
If overall speculative role is true,
how should cytokinin effect growth
directions to provide balance in the plant?
Cytokinin has been found to broaden plant parts, including leaves and stems. Should complementit's analogue deficiency signal strigolactones effect on plant growth. Strigolactones should lengthen plant cells and tissues.
Proven Synthesis and Transport
-
Made in high amounts in dividing shoot meristematic cells. 82 Why this makes sense - auxin and probably cytokinins, jasmonates and salicylic acid cause the the attraction of all nutrients to dividing cells including those in the shoot meristem. A high amount of minerals will exist then stimulate cytokinin synthesis which will attract even more minerals and other nutrients.
-
Made in the highest concentrations in the root meristematic cells. 83 Why this makes sense - roots will have the highest amount of minerals as of course this is where they first enter the plant.
Proven Effects
-
Exogenous CK inhibits senescence of leaves. 65 66 67 Why this makes sense - CK is an indication of excess or growth appropriate levels of minerals. These minerals need to be complemented by water, sugar and oxygen. Sugar and oxygen are made in the shoots, thus cytokinin acts to preserve them.
-
Induces new shoots in undifferentiated calluses. 115 Why this makes sense - See above.
-
Is integral to differentiation of the shoot meristem. 84 Why this makes sense - See above.
-
Stimulates the development of lateral buds and branching. 85 Why this makes sense - This is probably only true if there is a relative abundance of cytokinin over auxin and jasmonates indicating that the current shoot apical meristem directed growth is not meeting with the same success as the current root system. Thus the situation warrants other secondary meristems growing out and harvesting more auxin and making more sugar.
-
Induces cell broadening. 86 Why this makes sense - Cytokinin's broadening should complementit's deficiency signal partner strigolactones growth patterns which should be lengthening of plant parts.
-
Integral to root differentiation. 87 Why this makes sense - Cytokinin levels will determine presumably whether growth is strongly controlled by one root apical meristem like a Christmas tree or branching out.
-
Integral to leaf formation. 88 Why this makes sense - Should cause new leaves to be formed and should cause current ones to broaden catching more sunlight and harvesting more oxygen with both strategies.
-
Along with auxin, necessary to be present to induce cell division. 89 Why this makes sense - Unless there is a guaranteed surplus of minerals, oxygen, water and sugar, a plant knows it should not initiate new cells. Auxin and cytokinin would indicated the necessary amounts of minerals and oxygen. salicylic acid and jasmonate are probably also required before a plant starts a cell division.
-
Integral to chloroplast development 90 91 Why this makes sense - Again, minerals need to be complemented by water, oxygen, and sugar. Photosynthesis generates oxygen and sugar, so cytokinin is interested in maximizing this.